MeanShift
Published:

MindNote - Machine Learning - Unsupervised Learning - Clustering
Author: Christian M.M. Frey
E-Mail: christianmaxmike@gmail.com
Mean Shift
Recap on Kernel Density Estimation
The 1D kernel density estimation (KDE) model uses \(p (x^i) = \frac{1}{n} \sum_{j=1}^{n} k_\sigma (x^i-x^j)\)
where the PDF $k$ is the kernel and the parameter $\sigma$ is the bandwidth.
When using the (normlized) gaussian kernel
\[k_1(r) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} exp(- \frac{r^2}{2})\]Note that we can add a bandwidth (standard deviation) $\sigma$ to any PDF $k_1$, using
\(k_\sigma (r) = \frac{1}{\sigma} k_1 (\frac{r}{\sigma})\) which results for the gaussian kernel in the following
\[k_\sigma(r) = \frac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2 \pi}} exp (- \frac{r^2}{2 \sigma^2})\]Mean Shift procedure
The steps of the mean shift algorithm are as follows:
- For each data point x in our dataset D, we calculate the distance between x and every other point in D
- Calculate weights for each point in D by using a kernel (here we will use a gaussian kernel) of that point’s distance to x
- The kernel function penalizes points with increasing distance
- The rate at which the weights converge to zero is determined by the bandwidth (see above)
- Next, we update x as the weighted average of all other points in D
-> Following this procedure, the algorithm pushes points that are close together even closer until they reach a termination criterion.
Load dependencies
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns;
import numpy as np
from numpy import exp, sqrt, array, abs
sns.set()
import math
import matplotlib.cm as cm
Generate Data
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs
X, y_true = make_blobs(n_samples=300, centers=4, cluster_std=0.60, random_state=0)
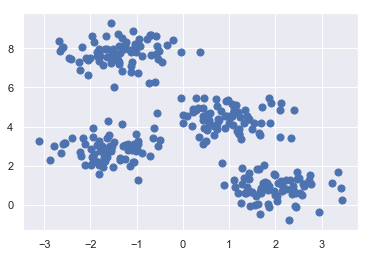
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=50);
Implementation of MeanShift with gaussian kernel
class MeanShift(object):
'''
Implementation of the MeanShift algorithm with a gaussian kernel
Arguments:
max_iter: maximal number of iterations
bandwidth: standard deviation of the gaussian kernel
tol: tolerance threshold
Properties:
max_iter: maximal number of iterations
bandwidth: standard deviation of the gaussian kernel
tol: tolerance threshold
'''
def __init__(self, max_iter=100, bandwidth=.5, tol=1e-5):
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.bandwidth = bandwidth
self.tol = tol
def distance(self, x, X):
'''
Calculates the euclidean distance between a datapoint x to all other points in the dataset, denoted as X
Arguments:
x: datapoint to which the distances will be calculated
X: the dataset including all datapoints
'''
return (sqrt((x-X)**2).sum(1))
def gaussian_kernel(self, d, bandwidth):
'''
Defines the gaussian kernel
Arguments:
d: distance
bandwidth: bandwidth defining the standard deviation of the gaussian kernel
'''
f_1 = 1.0/(bandwidth * math.sqrt(2*math.pi))
f_2 = exp(-0.5*((d/bandwidth))**2)
return f_1 * f_2
def _calc (self, x, X, bandwidth):
'''
calcuates the weighted average of all datapoints in X w.r.t to a certain datapoint x in X.
Arguments:
x: datapoint being currently considered
X: dataset
bandwidth: bandwidth for the gaussian kernel (smoothing factor)
'''
dist = self.distance(x, X)
weight = self.gaussian_kernel(dist, bandwidth)
return (weight[:, None]*X).sum(0) / weight.sum()
def _plot (self, X):
'''
simple plotting
'''
dist = self.distance([0,0], X)
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:, 1], s=25, c=dist, cmap='viridis')
def fit (self, X):
'''
Executes the MeanShift algorithm.
Arguments:
X: dataset
'''
it = 0
for i in range(self.max_iter):
X_adapted = np.array([self._calc(x,X,self.bandwidth) for x in X])
if it % 1 == 0:
self._plot(X_adapted)
if it >= self.max_iter or abs(X-X_adapted).sum()/abs(X.sum()) < self.tol:
print ("Convergence at iteration {}".format(it))
return X_adapted
X = X_adapted
it += 1
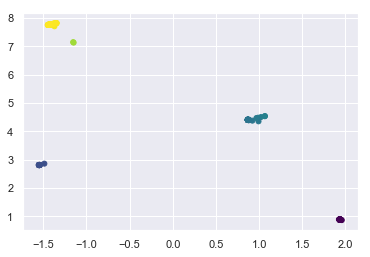
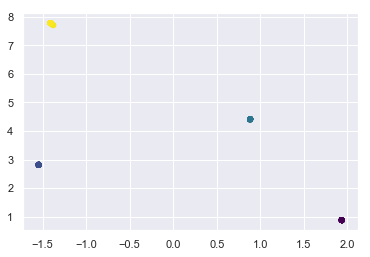
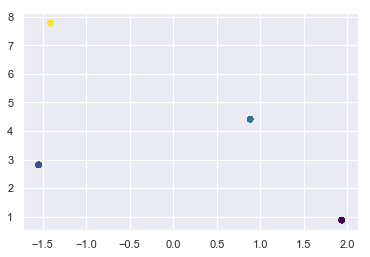
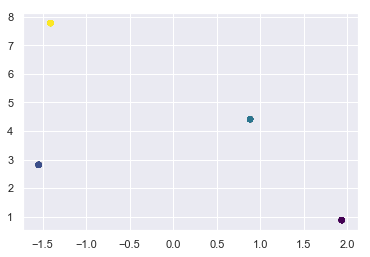
Run it
meanshift = MeanShift()
meanshift.fit(X);
Convergence at iteration 6
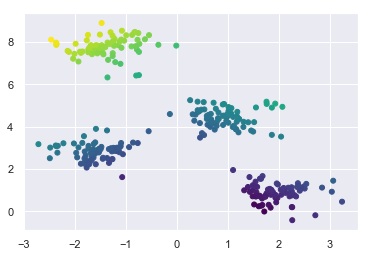
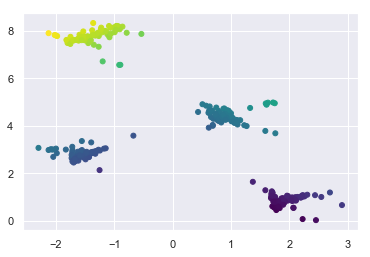
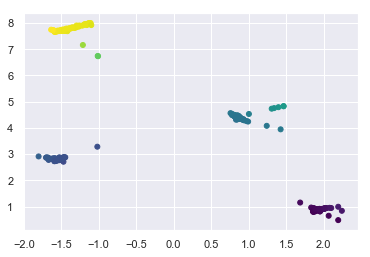
Advantages of MeanShift
- Clusters can have arbitrary shape and size and there are no restriction to convex shapes
- Number of clusters is determined autormatically
- Robustness against outliers
- Easy implementation and parallelisation
- Choice of kernel function
Additional notes
- published in: Dorin Comaniciu and Peter Meer. 2002. Mean Shift: A Robust Approach Toward Feature Space Analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24, 5 (May 2002), 603-619. DOI=http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/34.1000236
